The surprisingly complex inner workings of an endocrine tumor
Tokyo, Japan – There is strength in teamwork, and it turns out that this applies to tumors, too. Researchers from Japan have reported that different types of cells within a single benign tumor may work together to promote the tumor’s growth.
In a study published this month in Hypertension, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU)have revealed that a common hormone-producing tumor may actually be composed of a more complex collection of cells than previously thought.
Primary aldosteronism a type of high blood pressure that can be caused by tumors growing in the outer layer of the adrenal glands. These tumors, known as adenomas, produce a hormone called aldosterone that raises blood pressure and can cause other cardiovascular problems.
“Adrenal tumors include nonfunctional adenomas (NFAs), which do not produce aldosterone, and aldosterone-producing adenomas (APAs), which do,” explains lead author of the study Masanori Murakami. “At present, it was unclear whether all of the cells within an APA are involved in hormone production, or whether different cell types within APAs play different pathogenic roles.”
To investigate this, the researchers performed single-nucleus RNA sequencing. This involves extracting RNA from the nucleus and sequencing it to reveal which genes are active. The researchers analyzed the sequencing results to categorize the tumor cells based on their gene-expression profiles. All in all, the team sampled adrenal-gland tissue from two patients with NFAs and three patients with APAs.
“The results were striking,” says Tetsuya Yamada, senior author. “We identified 13 clusters, some of which expressed genes associated with hormone production, especially CYP11B2, which encodes an enzyme that produces aldosterone.”
Simulated analysis of how these different cell types interacted and changed in the differentiation process identified two cell-fate pathways in APAs, both of which were involved in hormone production but expressed different sets of genes. As the cells differentiated, they expressed even higher levels of genes involved in aldosterone synthesis and became increasingly active.
“The identification of two distinct cell fates in APAs suggests that these tumors have a complex cellular composition that contributes to their growth, development, and effect on the clinical characteristics,” says Murakami.
In addition to CYP11B2, cells later in the cell-fate pathway also expressed more CYP17A1, which contributes to cortisol synthesis, possibly explaining the small amounts of excessive cortisol produced in some patients with APA. Furthermore, cellular clusters with active hormone production display an augmented expression of ribosome-related genes, indicative of increased transcriptional activity at single-nucleus level.
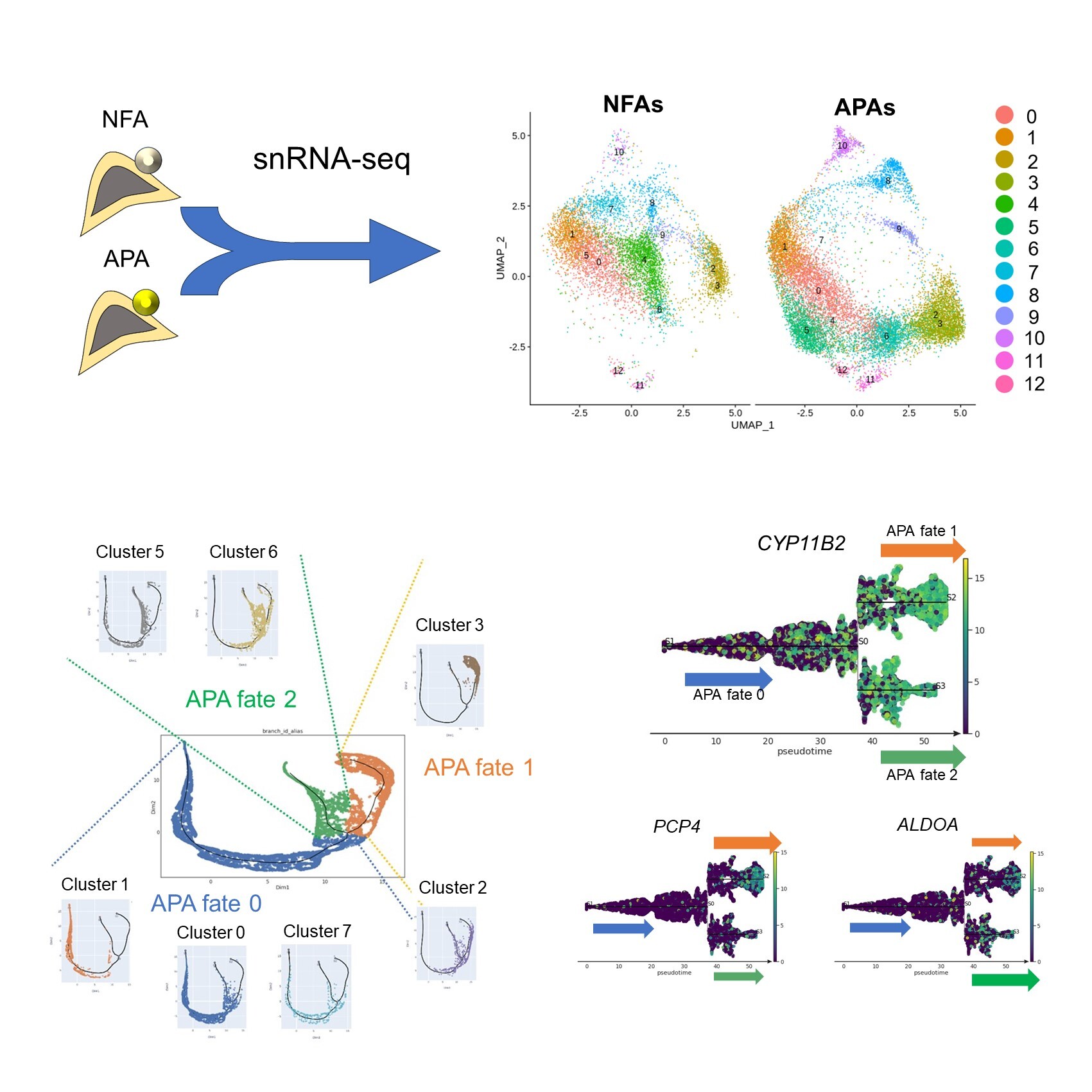
Overview of the present study.
Single-nucleus RNA sequencing of 2 nonfunctional adenomas and 3 aldosterone-producing adenomas revealed 13 clusters (Upper). Pseudotime course analysis predicted the transition of two cell fates in APAs (Lower).
Summary
Journal Article
TITLE:Single-Nucleus Analysis Reveals Tumor Heterogeneity of Aldosterone-Producing Adenoma
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.21446
Correspondence to
Tetsuya Yamada, MD, PhD, Professor
Masanori Murakami, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor
Department of Molecular Endocrinology and Metabolism,
Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences,
Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU)
E-mail:tyamada.mem(at)tmd.ac.jp
E-mail:mmurakami.mem(at)tmd.ac.jp
*Please change (at) in e-mail addresses to @ on sending your e-mail to contact personnels.

