“Discovery of a novel function of dendritic cells to fine-tune excessive immune responses”

Toshiaki OHTEKI
Professor, Department of Biodefense Research,
Medical Research Institute
Highlights
| 1. | An immune response is a double-edged sword that simultaneously defends and injures the host; the more severe the infection, the greater the regulatory control must be. |
| 2. | Our research group discovered that hemophagocytosis by dendritic cells moderates immune responses to ensure the host’s survival. |
| 3. | Our findings may lead to hemophagocytosis-based diagnostic and therapeutic applications for viral infections and autoimmune diseases. |
Main findings and significance of this study
In summary, our findings indicate that hemophagocytosis is induced by TLR ligands or viruses in sequential steps (Fig. 4) to suppress potentially damaging immune responses.
Figure
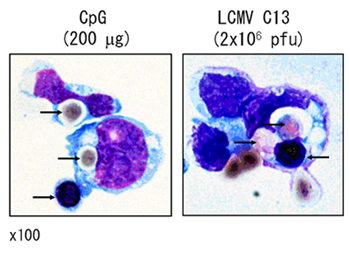
Figure 1. Hemophagocytosis by Mo-DCs.
Sorted hemophagocytes from the bone marrow of CpG-injected or LCMV C13-infected mice were stained with Diff-Quick. Black arrows indicate hemophagocytosed and attached erythroid cells. Original magnification, x100.
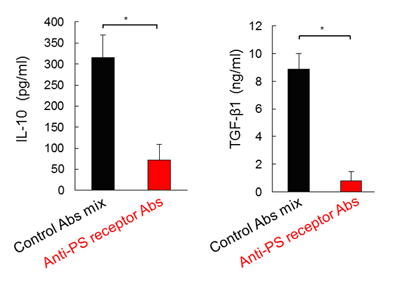
Figure 2. Hemophagocytosis-dependent IL-10 and TGF-β1 production.
Amount of serum IL-10 and TGF-β1 24 h in WT mice after LCMV C13 infection, which was injected with an isotype-control Ab cocktails or Abs that block PS receptors (500 μg each).
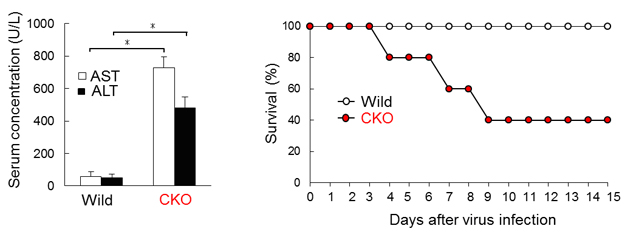
Figure 3. Hemophagocytosis fine-tunes immune responses in viral infection.
Amount of serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), indicators of liver damage, in WT and CKO mice 9 days after infection with LCMV C13, and the survival (%) of WT or CKO mice after infection.
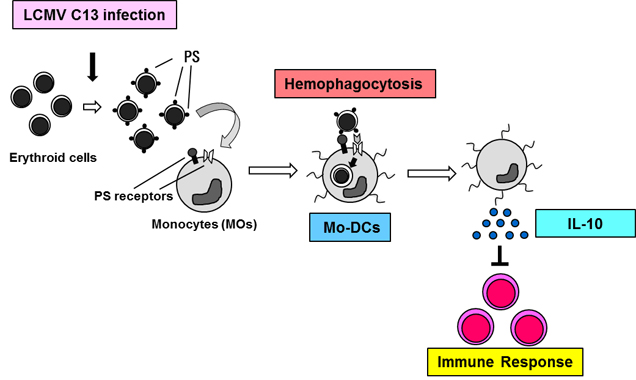
Figure 4. The development and role of hemophagocytosis in immune responses.
Type I IFNs produced in response to LCMV C13 infection induce phosphatidylserine (PS) on erythroid cells and PS receptors on Mo-DCs. Mo-DCs perform hemophagocytosis and release the immunoregulatory cytokine IL-10 to fine-tune immune responses, including CTL activity.
Correspondence to:
Department of Biodefense Research
Medical Research Institute, Tokyo Medical and Dental University
1-5-45 Yushima, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8510, Japan
E-mail: ohteki.bre(at)mri.tmd.ac.jp
*Please change (at) in the e-mail addresses to @ when sending correspondence.

