That’s so meta(transcriptomics): distinctive bacterial taxonomic and functional profiles in mouth disease
Published: October 28, 2021
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that a characteristic shift in bacterial community composition and function marks progression from a healthy mouth to periodontal disease
Tokyo, Japan - When you’re smiling, the whole world smiles with you; but what happens when gum or tooth disease starts to dim your pearly whites? Now, researchers from Japan have found a bacterial signature that marks the shift from healthy teeth and gums to periodontitis.
In a study published in mSystems, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that specific bacterial signatures differentiate healthy mouths from those with gingivitis and periodontitis.
Periodontal disease is inflammation of the gums caused by infection with many different kinds of bacteria. The infection begins at the gum line and then makes its way down into the bones of the jaw, where it can cause permanent damage and tooth loss.
“Previous studies have explored the differences in bacterial communities in healthy mouths or those affected by gingivitis or periodontitis,” says lead author of the study Takashi Nemoto. “However, it was unclear how the metabolic activities of these communities changed during the progression from health to periodontitis, so we wanted to investigate the functional profiles of these communities.”
To do this, the researchers took plaque samples from three sites within the mouths of 21 patients with periodontal disease: from a healthy site, from a site showing gingivitis, and from a site with periodontitis. They then performed a specialized analysis called metatranscriptomic analysis to determine what functional substances the bacteria at these sites were producing, as well as a lineage analysis to determine what types of bacteria were present at these sites.
“The results showed clear differences in both bacterial community composition and functional profiles between health and diseased sites,” explains Takanori Iwata, senior author. “Importantly, we found that the transcriptional activity of taxa including Eubacterium nodatum, Eubacterium saphenum, Filifactor alocis, and Fretibacterium fastidiosum was higher than that of well-known periodontopathic bacteria (red complex; Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, and Treponema denticola) at diseased sites than at healthy sites, and as gingivitis progressed to periodontitis.”
These changes indicate that these taxa are associated with the progression of periodontal disease, and that dynamic changes occur in the oral microbiome as periodontal disease worsens.
“The changes that we observed in the transcriptional activity of these taxa with disease progression show that the shift from health to periodontitis is accompanied by changes in both the structure and the complexity of the bacterial network,” says Nemoto.
Given that gingivitis is reversible, but periodontitis is not, the identification of key bacterial species and functions involved in the progression from a healthier state to a diseased state could help prevent permanent damage.
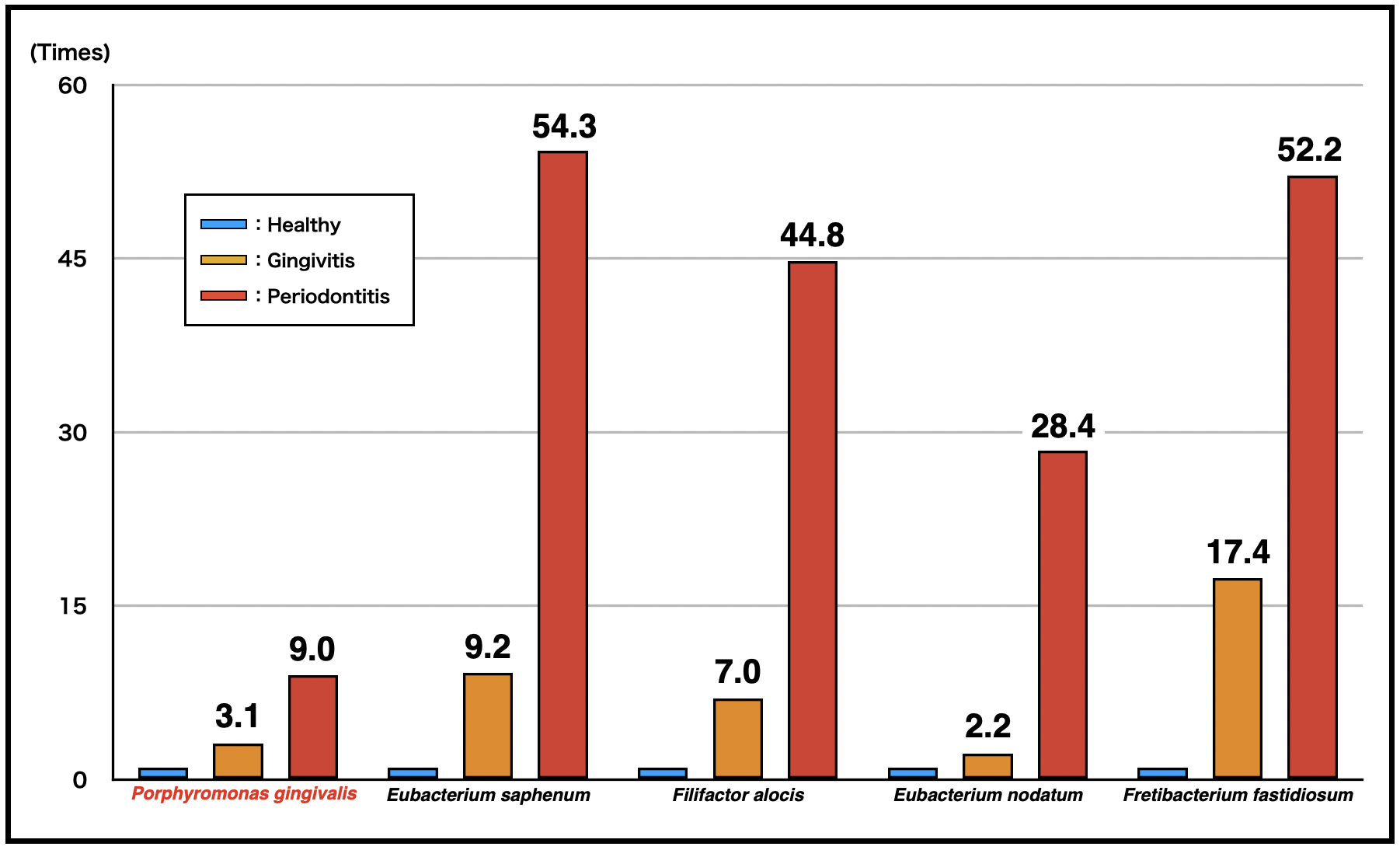
Figure 1. Change in bacterial activity per site
The bacterial activity of a healthy site was defined as 1. The activities of several taxa were higher than that of red complex bacteria (e.g., Porphyromonas gingivalis).
The bacterial activity of a healthy site was defined as 1. The activities of several taxa were higher than that of red complex bacteria (e.g., Porphyromonas gingivalis).
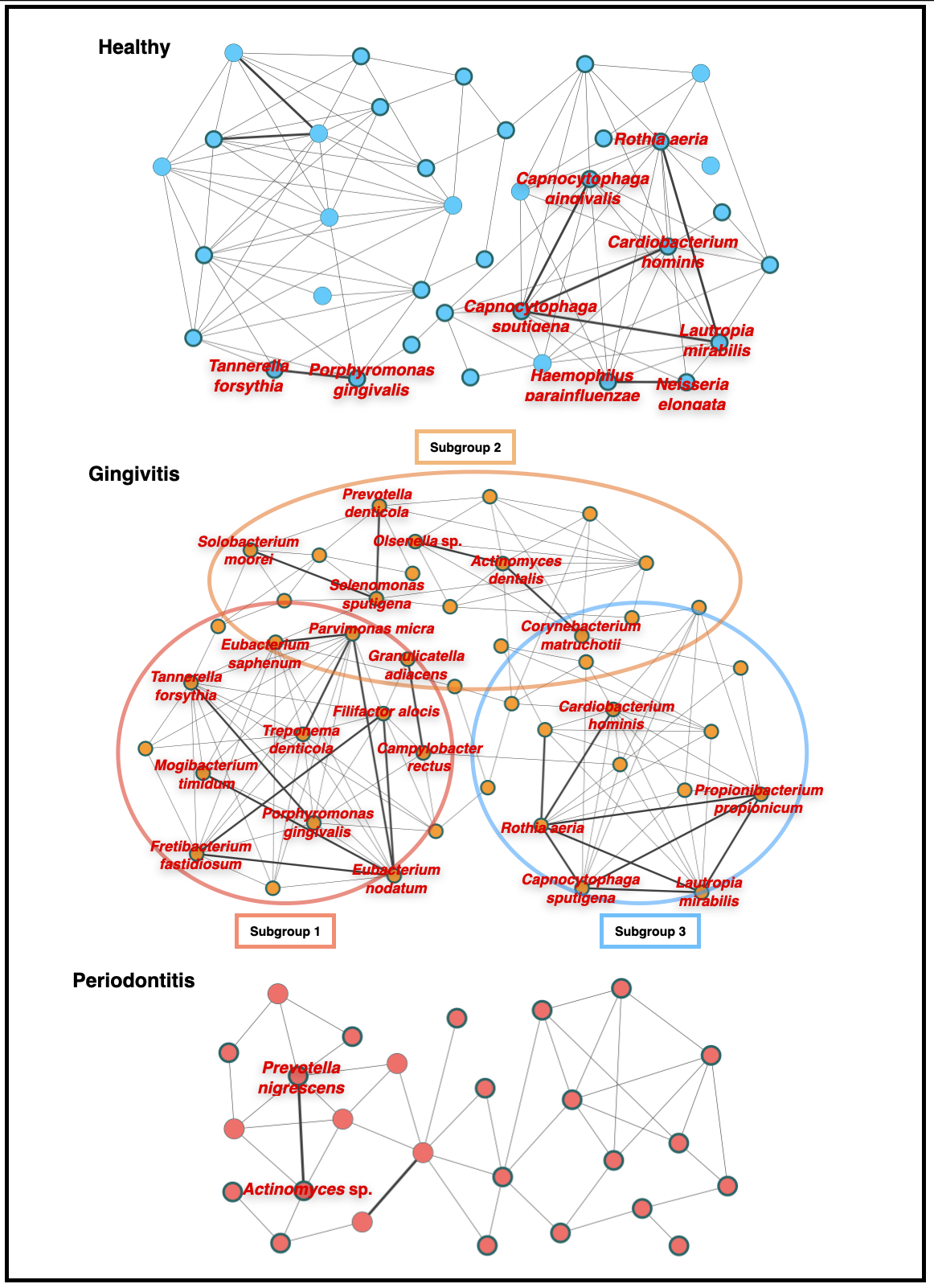
Figure 2. Bacterial co-occurrence networks
Each bacterial species and co-occurrence relationship are indicated by a node and an edge, respectively. Bacterial species with significant-high activity are indicated with bold circles, and interactions with significant co-occurrence are indicated with bold lines. Core bacterial species that are shown significant-high activity and significant co-occurrence interactions with other bacteria are indicated in red letters. The gingivitis co-occurrence network appeared to comprise three subnetworks. Subgroup 1 included the species mainly exhibited co-occurrence relationships with red complex bacteria; these species were detected in both gingivitis and periodontitis sites. Subgroup 2 included the species detected mainly in gingivitis sites. Subgroup 3 included mainly the species detected mainly in both healthy and gingivitis sites.
Each bacterial species and co-occurrence relationship are indicated by a node and an edge, respectively. Bacterial species with significant-high activity are indicated with bold circles, and interactions with significant co-occurrence are indicated with bold lines. Core bacterial species that are shown significant-high activity and significant co-occurrence interactions with other bacteria are indicated in red letters. The gingivitis co-occurrence network appeared to comprise three subnetworks. Subgroup 1 included the species mainly exhibited co-occurrence relationships with red complex bacteria; these species were detected in both gingivitis and periodontitis sites. Subgroup 2 included the species detected mainly in gingivitis sites. Subgroup 3 included mainly the species detected mainly in both healthy and gingivitis sites.
###
The article, “Discrimination of Bacterial Community Structures among Healthy, Gingivitis, and Periodontitis Statuses through Integrated Metatranscriptomic and Network Analyses,” was published in mSystems at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00886-21.
Summary
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have found that the transcriptional activity of taxa including Eubacterium nodatum, Eubacterium saphenum, Filifactor alocis, and Fretibacterium fastidiosum was higher than that of well-known periodontopathic bacteria at diseased sites than at healthy sites in the mouth, indicating that changes in the oral microbiome during disease progression includes alterations of both the structure and the complexity of bacterial networks.
Journal Article
JOURNAL: mSystems
TITLE:Discrimination of Bacterial Community Structures among Healthy, Gingivitis, and Periodontitis Statuses through Integrated Metatranscriptomic and Network Analyses
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00886-21
TITLE:Discrimination of Bacterial Community Structures among Healthy, Gingivitis, and Periodontitis Statuses through Integrated Metatranscriptomic and Network Analyses
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00886-21

