“Periodic injections of synovial stem cells inhibit osteoarthritis progression in the knee”
- Trophic factors for chondroprotection are revealed –
Points
| ● | We developed a novel treatment strategy in rat models against knee osteoarthritis, which 8.5 million patients suffer from in Japan. |
| ● | Periodical intra-articular injections of synovial stem cells prevented the progression of osteoarthritis in rats. |
| ● | Synovial stem cells produced many kinds of trophic factors for chondroprotection. |
| ● | This treatment is clinically possible against knee osteoarthritis. |
Professor Ichiro Sekiya and Assistant Professor Nobutake Ozeki at the Center for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that periodical intra-articular injections of synovial stem cells derived from the knee synovium prevented the progression of knee osteoarthritis (OA) in a rat model. Generally, the number of cells rapidly decreased after an injection, which means the minimum effect of single injection against the chronic pathology of knee OA. On the other hand, periodical injections were effective. Most of the injected cells adhered to the synovium, then produced many kinds of the trophic factors with chondroprotective effects. This study was supported by the Highway Program for Realization of Regenerative Medicine from Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) and Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED. This will be online published on “Osteoarthrisi and Cartilage” at AM 11:00 on February 12th, 2016 (UTC+0).
Background
OA is a degenerative joint disease which 8.5 million patients suffer from in Japan. Due to its complicated pathology, no effective treatment has been established. Our group have been transplanted synovial stem cells to the cartilage and meniscal defect. The purpose of this study was to develop the effective procedure for the prevention of OA, and to reveal the mechanism of the procedure.
Summary of findings
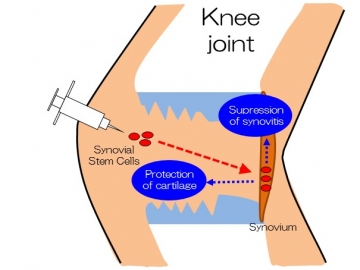
Cartilage degeneration and synovitis were observed at 8 weeks after the transection of the anterior cruciate ligament of rats. OA changes were suppressed when one million synovial MSCs were weekly injected into the knee joint after the surgery. A single injection had a minimum chondroprotective effect. In vivo bioluminescent imaging demonstrated that synovial stem cells rapidly decreased at 7 days but weekly injections of synovial MSCs maintained viable cells in the knees. Histological and flow cytometric analyses of LacZ and GFP expressing synovial MSCs revealed that injected MSCs migrated mainly into the synovium and most of them retained their undifferentiated MSC properties. Species-specific microarray and PCR analyses showed that the human mRNAs on day 1 for 1060 genes increased over 2-fold, and increased the expressions of PRG-4, BMP-2, and BMP-6 genes encoding chondroprotective proteins, and TSG-6 encoding an anti-inflammatory one. Injected cells had important roles for the protection of cartilage and suppression of synovitis, maintaining their stem cell properties.
Significance
Recently, a single injection of adipose stem cells against knee OA has been performed as an extra-ordinary treatment in Japan. However, a single injection for the chronic pathology is insufficient and the mechanism of the treatment was unclear. This animal study revealed that periodical injections had definite effect for the prevention of knee OA. Our group have a plan for the clinical study of periodical injections of synovial stem cells for the treatment of knee OA.
Correspondence to
About the experiments
Center for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU)
Ichiro Sekiya
TEL:+81-3-5803-4017 FAX:+81-3-5803-0192
E-mail:saisei01.arm(at)tmd.ac.jp
Ichiro Sekiya
TEL:+81-3-5803-4017 FAX:+81-3-5803-0192
E-mail:saisei01.arm(at)tmd.ac.jp
About the transgenic rats
Department of Organ Fabrication, Keio University School of Medicine
Eiji Kobayashi
TEL: +81-3-5315-4090 (63968) FAX: +81-3-5315-4089
E-mail:organfabri(at)keio.jp
Eiji Kobayashi
TEL: +81-3-5315-4090 (63968) FAX: +81-3-5315-4089
E-mail:organfabri(at)keio.jp
About the press release
Public Relations Office, Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU)
1-5-45 Yushima, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8510
E-mail:kouhou.adm(at)tmd.ac.jp
Public Relations Division, Japan Science and Technology Agency
5-3 Yonbancho, Chiyoda-ku, 102-8666 Tokyo
TEL:03-5214-8404 FAX:03-5214-8432
E-mail:jstkoho(at)jst.go.jp
1-5-45 Yushima, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8510
E-mail:kouhou.adm(at)tmd.ac.jp
Public Relations Division, Japan Science and Technology Agency
5-3 Yonbancho, Chiyoda-ku, 102-8666 Tokyo
TEL:03-5214-8404 FAX:03-5214-8432
E-mail:jstkoho(at)jst.go.jp
About AMED
Department of Planning and Management, Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
20F Yomiuri Shimbun Bldg. 1-7-1 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, 100-0004 Japan
TEL: +81-3-6870-2220 FAX: +81-3-6870-2243
E-mail:saisei(at)amed.go.jp
*Please change (at) in the e-mail addresses to @ when sending correspondence.
20F Yomiuri Shimbun Bldg. 1-7-1 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, 100-0004 Japan
TEL: +81-3-6870-2220 FAX: +81-3-6870-2243
E-mail:saisei(at)amed.go.jp
*Please change (at) in the e-mail addresses to @ when sending correspondence.

