A Nice Reactive Ring to It: New Synthetic Pathways for Diverse Aromatic Compounds
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have introduced a new synthetic process for producing an important family of carbon-based molecules known as γ-aryl-β-ketoesters. These molecules are used in the production of many vital pharmaceuticals, including alectinib, which is administered to treat non-small-cell lung cancer, and Januvia, a diabetes drug. This chemical approach may help in the preparation of a diverse range of their analogs and many other medication candidates more quickly.
Organic chemistry, which studies reactions involving carbon-based molecules, is central to the pharmaceutical industry. Certain reactions, such as the formation of multi-substituted aromatic compounds, are essential to the production of a variety of drugs. One important class of molecules that can be utilized as versatile intermediates are the γ-aryl-β-ketoesters. However, it was difficult to synthesize a variety of these critical molecules. In a study published in Organic Letters at October 24, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) report a new reaction pathway to easily produce γ-aryl-β-ketoesters. To do this, they utilized aryne chemistry, which involves the removal of two substituents from a benzene ring, yielding a very reactive chemical species. “To successfully synthesize the γ-aryl-β-ketoesters, we decided to use a pathway that involves γ-aryl-β-ketoester-type arynes, because they are useful intermediates for creating multi-substituted aromatic derivatives,” says first author Keisuke Uchida.
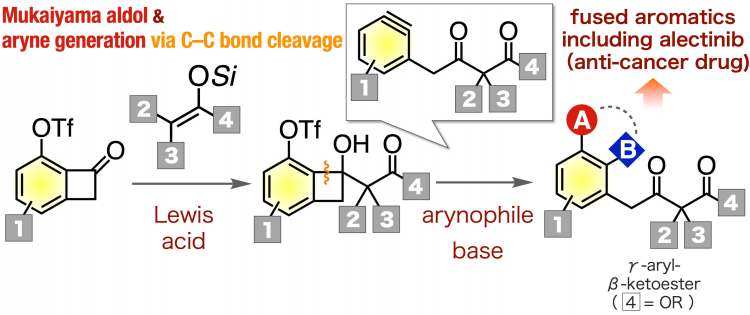
Figure:A synthetic method for diverseγ-aryl-β-ketoesters throughγ-aryl-β-ketoester-type arynes triggered by carbon–carbon bond cleavage.
The Mukaiyama aldol reaction of 6-(triflyloxy)benzocyclobutenones with ketene silyl acetals and subsequent generation of γ-aryl-β-ketoester-type arynes from resulting 6-(triflyloxy) benzocyclobutenols in the presence of arynophiles efficiently provided a wide range of γ-aryl-β-ketoesters. The method was applicable to the synthesis of an analog of ALK inhibitor.
The article “Synthesis of Diverse γ-Aryl-β-ketoesters via Aryne Intermediates Generated by C-C Bond Cleavage” was published in Organic Letters at DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03418
Summary
Correspondence to
Department of Chemical Bioscience,
Institute of Biomaterials and Bioengineering,
Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU)
E-mail:thosoya.cb(at)tmd.ac.jp
*Please change (at) in e-mail addresses to @ on sending your e-mail to contact personnels.

