"Small populations of normal cells affect immunity in patients with XLP1"
Tokyo, Japan – Human SH2D1A mutations resulting in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome type 1 (XLP1) are associated with a unique susceptibility to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which may lead to fatal infectious mononucleosis (FIM). Many studies have attempted to elucidate an appropriate treatment for XLP1 that does not involve hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT); clinical evidence supporting such treatments has been minimal, until now.
In a new study published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, an international research team led by experts from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) investigate the mechanism of mild disease presentation in a family with XLP1 that did not undergo HSCT, and found evidence of somatic reversion, or a return to normal expression levels, of SLAM-associated protein (SAP) in T cells.
Patients with XLP1 are susceptible to severe complications of EBV infections, such as FIM, which has a high mortality rate. This is attributed to poor activation and cytotoxicity of the CD8+ T cell. The only effective treatment for XLP1 has been HSCT. Unfortunately, HSCT has a high risk of treatment-related mortality and many side effects.
“We analyzed the clinical features of 40 Japanese patients with XLP1,” says Hirokazu Kanegane, corresponding author on the study. “We identified a family that did not experience FIM, although none of the members had undergone HSCT.”
In the study, whole-exome sequencing of patients in the family with mild disease revealed a known mutation, which reduced the expression of SAP in T cells in affected patients. This conflicted with the mild disease presentation.
“We performed more detailed analyses of T cells in the affected family, and found small populations of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing functional SAP at normal levels,” says Akihiro Hoshino, lead author on the study. “Because this somatic reversion was present in multiple patients in the same family, it may be an inherited characteristic.”
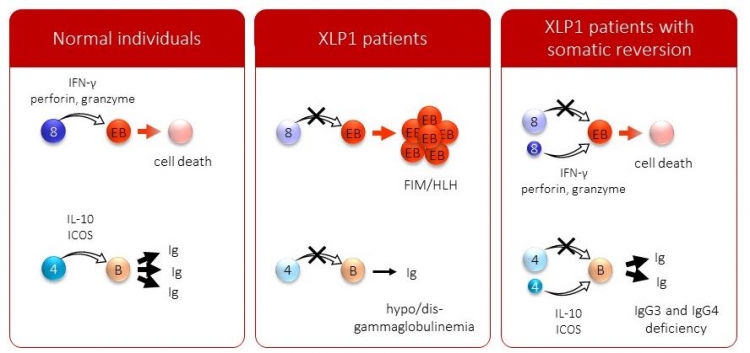
Fig:Model of cellular and humoral immunity
This slide illustrates a model of cellular and humoral immunity regarding SAP. In normal individuals, SAP+ CD8+ T cells attack EBV-infected B cells via IFN-gamma, perforin, and granzyme, and EBV-infected B cells lead to cell death. SAP+ CD4+ T cells help immunoglobulin production from B cells via IL-10 and ICOS. In XLP1 patients, the SAP function is completely impaired, and the patients develop FIM or HLH and hypo- or dysgammglobulinemia. In XLP1 patients with somatic reversion, as demonstrated in this study, small populations of SAP+ T cells can rescue the function. The patients were not associated with FIM or HLH, and they presented with IgG3 and IgG4 deficiency only.
XLP1 is a disease with deficient immunity against EBV, which can result in fatal outcomes. Treatment has been limited to HSCT, which can be a dangerous approach. This study showed that small populations of normal T cells could reduce the severity of disease, suggesting that less invasive therapies may be useful in treatment of XLP1.
The article, "Modification of cellular and humoral immunity by somatically reverted T cells in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome type 1," was published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology at DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.07.044
Summary:
Correspondence to:

Department of Child Health and Development,
Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences,
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU)
E-mail:hkanegane.ped(@)tmd.ac.jp

