"How does estrogen protect bones? Unraveling a pathway to menopausal bone loss"
Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and The University of Tokyo find a connection between estrogen and bone health that may offer a new way to treat osteoporosis in women experiencing menopause
Tokyo–Osteoporosis is a condition in which bones become weak and prone to fractures. Fractures typically occur in the wrist, spine, or hip, and can often lead to permanently impaired mobility. Women over 50 are at a high risk of developing osteoporosis, which may be due to the loss of estrogen that occurs after menopause. While studies have linked estrogen levels to bone health, the exact details of this connection are not entirely clear. Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe a new molecular link between estrogen and bone aging, which may eventually lead to new strategies to treat postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Bone is a complex tissue, consisting of a matrix of proteins and minerals that give it the flexibility and strength to support body movement. Bone also contains several types of specialized cells, including osteocytes, that help to maintain this matrix. Over a person’s lifetime, many factors can affect how healthy bone structure is maintained. One of these factors is the female sex hormone, estrogen.
“Over the last few decades, we’ve learned that estrogen plays an important role in maintaining a functional bone matrix,” corresponding authors Tomoki Nakashima and Hiroshi Takayanagi explain. “Exactly how estrogen does this, though, is not fully understood. Our laboratory recently discovered that bone matrix is maintained by a protein called Sema3A, which is secreted by osteocytes. This led us to suspect that there might be a mechanistic relationship between estrogen and Sema3A.”
Sema3A does indeed appear to be linked to estrogen: the researchers found that blood serum levels of the protein decrease in premenopausal women as they get older—and drop even further once women reach menopause. But how, at the biological level, are estrogen and Sema3A related? And what is Sema3A doing in bone tissue?
To answer these questions, the researchers turned to mice. When mice are given an ovariectomy (that is, when their ovaries are removed), the loss of estrogen causes their bone mass to decrease. This can be prevented, however, by giving the mice an extra supply of the hormone. The team took advantage of this to explore the function of Sema3A.
“When we genetically removed Sema3A from the osteoblast lineage cells (including osteocytes) of mice, we found that intravenous estrogen no longer prevented bones from deteriorating after an ovariectomy,” lead author Mikihito Hayashi describes. “In addition, we found that Sema3A sets off a chain of signaling events that promote the survival of osteocytes in these mice. This suggests that Sema3A serves as a key mechanistic link between estrogen and bone maintenance .
Tokyo–Osteoporosis is a condition in which bones become weak and prone to fractures. Fractures typically occur in the wrist, spine, or hip, and can often lead to permanently impaired mobility. Women over 50 are at a high risk of developing osteoporosis, which may be due to the loss of estrogen that occurs after menopause. While studies have linked estrogen levels to bone health, the exact details of this connection are not entirely clear. Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe a new molecular link between estrogen and bone aging, which may eventually lead to new strategies to treat postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Bone is a complex tissue, consisting of a matrix of proteins and minerals that give it the flexibility and strength to support body movement. Bone also contains several types of specialized cells, including osteocytes, that help to maintain this matrix. Over a person’s lifetime, many factors can affect how healthy bone structure is maintained. One of these factors is the female sex hormone, estrogen.
“Over the last few decades, we’ve learned that estrogen plays an important role in maintaining a functional bone matrix,” corresponding authors Tomoki Nakashima and Hiroshi Takayanagi explain. “Exactly how estrogen does this, though, is not fully understood. Our laboratory recently discovered that bone matrix is maintained by a protein called Sema3A, which is secreted by osteocytes. This led us to suspect that there might be a mechanistic relationship between estrogen and Sema3A.”
Sema3A does indeed appear to be linked to estrogen: the researchers found that blood serum levels of the protein decrease in premenopausal women as they get older—and drop even further once women reach menopause. But how, at the biological level, are estrogen and Sema3A related? And what is Sema3A doing in bone tissue?
To answer these questions, the researchers turned to mice. When mice are given an ovariectomy (that is, when their ovaries are removed), the loss of estrogen causes their bone mass to decrease. This can be prevented, however, by giving the mice an extra supply of the hormone. The team took advantage of this to explore the function of Sema3A.
“When we genetically removed Sema3A from the osteoblast lineage cells (including osteocytes) of mice, we found that intravenous estrogen no longer prevented bones from deteriorating after an ovariectomy,” lead author Mikihito Hayashi describes. “In addition, we found that Sema3A sets off a chain of signaling events that promote the survival of osteocytes in these mice. This suggests that Sema3A serves as a key mechanistic link between estrogen and bone maintenance .
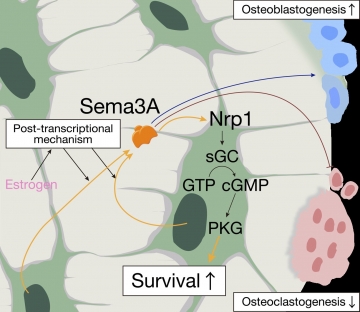
Title: Autoregulation of osteocyte Sema3A in bone homeostasis
Estrogen induces osteocyte expression of Sema3A, which acts on its receptor on osteocytes to promote survival, resulting in reduced osteoclastic bone resorption and enhanced osteoblastic bone formation. Sema3A-activated sGC–cGMP signaling through Nrp1 protected osteocytes from apoptosis.
We believe that, as women lose estrogen with age and Sema3A levels drop off, osteocytes begin to die and bone loses the ability to maintain its supportive structure.”
The researchers hope that the discovery of Sema3A as a major player in bone health and the signaling molecules it controls in bone may offer new therapeutic approaches to treating osteoporosis.
The article, “Autoregulation of osteocyte Sema3A orchestrates estrogen action and counteracts bone aging” was published in Cell Metabolism at DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.12.021.
The researchers hope that the discovery of Sema3A as a major player in bone health and the signaling molecules it controls in bone may offer new therapeutic approaches to treating osteoporosis.
The article, “Autoregulation of osteocyte Sema3A orchestrates estrogen action and counteracts bone aging” was published in Cell Metabolism at DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.12.021.
Summary:
Women who have reached menopause are at a greater risk of developing osteoporosis, which can lead to bone fractures and long-term impairment of mobility. Studies have suggested a link between reduced bone density and low estrogen levels due to menopause, but the basis for this link is unclear. Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University found that the protein Sema3A plays a key role in maintaining healthy bones, suggesting a new therapeutic avenue to treat osteoporosis.
Correspondence to

Tomoki Nakashima, Ph.D., Professor
Department of Cell Signaling,
Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences,
Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU)
E-mail:t.naka.csi(at)tmd.ac.jp
Department of Cell Signaling,
Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences,
Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU)
E-mail:t.naka.csi(at)tmd.ac.jp

