Identification of therapeutic targets for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus

Fumiaki Ando
Specially Appointed Assistant Professor of Nephrology at TMDU
After graduating from TMDU in 2008, I accumulated five years of clinical experience as a physician. I started my research career in 2013 and received a PhD in 2017. I was then assigned to become the Specially Appointed Assistant Professor of Nephrology and was also elected to the Candidates of Innovating Medical Scientist at TMDU. One of the goals of our laboratory’s research is to develop a definitive treatment for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI).
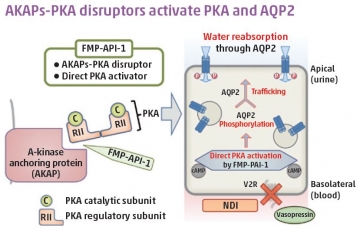
Congenital NDI is characterized by defective urine-concentrating ability.Daytime polyuria with nocturia significantly reduces a patient’s quality of life. In healthy patients, in response to dehydration, the antidiuretic hormone vasopressin binds to the vasopressin type 2 receptor (V2R) in renal collecting ducts and increases water reabsorption by rapid translocation of aquaporin-2 (AQP2) water channels to apical plasma membranes. Most cases of congenital NDI are caused by mutations to V2R that cause a loss of function, resulting in unresponsiveness to vasopressin.
We found novel therapeutic molecules of congenital NDI that can activate AQP2 by bypassing defective V2R signaling. The classic calcium-signal transducer, Wnt5a, activated AQP2 through calcineurin (Nat. Commun., doi:10.1038/ncomms13636). Screening for calcineurin activators is a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of congenital NDI. In renal collecting ducts, calcineurin is co-localized with A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs).AKAPs regulate the intracellular distribution and substrate specificity of protein kinase A (PKA). We next focused on the inhibition of AKAPs binding to PKA and found that AKAPs-PKA disruptors activated PKA and AQP2 to the same extent as vasopressin (Nat. Commun., doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03771-2).AKAPs-PKA disruptors are a potential novel category of therapeutic drugs for congenital NDI and other PKA-related diseases. We are now developing more potent compounds that will be effective in specific target issues.