Three-dimensional MRI offers new insights into globe shape evaluation in ocular diseases
PDF Download
- Globe shape evaluation

Kyoko Ohno-Matsui
Professor of Ophthalmology and Visual Science at TMDU
Profile
Dr. Ohno-Matsui graduated from the Faculty of Medicine at Yokohama City University, and received her MD and PhD at TMDU. She became Assistant Professor at TMDU in 1997, and Associate Professor in 2005. She took office as Professor in 2014 and leads the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science as Chairperson.
A:Pathologic myopia causes blindness. With fellow researchers in Japan and around the world, we have demonstrated that diverse ocular shapes are linked to the advance of disease. We used three-dimensional magnetic resonance
imaging (3D MRI) to examine 44 highly myopic patients and found that their eyes presented with symmetric nasal or posterior forms with barrel or cylindrical shapes, or were asymmetric and nasally or temporally misshapen, compared with normal, spherical emmetropic eyes. Characterizing ocular shape is critical for identifying preventive measures.
We also examined 105 patients to standardize definitions of posterior staphylomas in pathologic myopia. Panoramic OptosTM phthalmoscopy fundus images, similar to conventional clinical images and infrared images, identified ocular staphyloma edges by irregularities in pigmentation, reflectance, and fluorescence. The 3D MRI results corresponded well with fundus images of bnormalities in patients with wide or narrow macular staphylomas, or inferior or peripapillary staphylomas. Patients without staphylomas could be accurately identified. Patients with staphylomas were older and suffered from worse vision than those without.
A: Having global collaborators in places such as the United States, Australia, Singapore, and Europe, helps extend the work’s international implications. With my colleagues, we have proposed international photographic classification systems for myopic maculopathy characterized by pathologic myopia, posterior staphylomas and posterior lesions. Our system of numerical grouping based on disease severity established a moderately uniform categorization of 100 images by inter- and intra-consensus.
A: Three-dimensional MRI renders holistic topographical images using volume-depicting techniques rapidly and non-invasively. Computerized analyses provide signal strength-based semi-automatic delineation of global boundaries. Using 3D MRI facilitates early identification and management of vision field flaws.
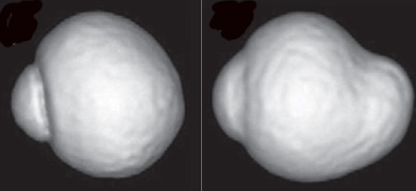
3D MRI image of the eye (nasal view)
A normal emmetropic eye is almost spherical (left). An eye with pathologic myopia (right), where the globe is deformed and the posterior segment forms a protruding pouch (known as posterior taphyloma).
A: There is a significant focus on translational ophthalmological research at TMDU. I have worked in close association with the High Myopia Clinic at TMDU. Research examining possible associations between eye shape and orbital shape is also underway here.
A: Future research may include longitudinal studies to characterize shape alterations of human eyes with age, identifying the first signs of myopia and elucidating mechanisms underlying pathologic myopia. A challenge would be to find suitable animal models on which to study pathologic myopia.
establishing homogeneous classification methods for myopic maculopathy, given its high prevalence here in East Asia. The roposed
classification systems will boost further studies in ocular disease.
Journal Information
Ophthalmology, doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.01.018
Proposed Classification of Posterior Staphylomas Based on Analyses of Eye Shape by Three-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Wide-Field Fundus Imaging
Ophthalmology, doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.03.035
Updates of pathologic myopia
Am. J. Ophthalmol., doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2015.01.022

