Breast reconstruction

We mainly perform primary reconstruction (simultaneous reconstruction) in accordance with breast surgeon.
Timing
-
-
Incision of SSM, and NSM
a. Primary reconstruction
Since 1998, we started Skin-sparing mastectomy (SSM), or Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) to reconstruct more beautiful breast. If you hope primary reconstruction, please consult breast surgery unit.
b. Secondary reconstruction
We can reconstruct the mastectomy defect or the partial defect after breast preserving surgery. After postoperative adjuvant therapy (chemotherapy radiotherapy), pleaase consult us.
Methods
a. Breast implant
-

cohesive implant
The advantage is not increasing the scar of the body. In many cases we select two-staged reconstruction. We insert an expander in the primary operation and replace it to cohesive gel silicone implant 4 to 6 months after 1st stage.
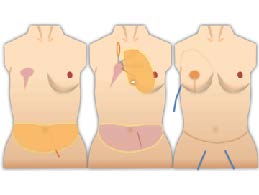
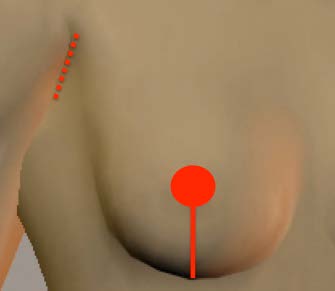
b. Autologous tissue
The advantage is making more natural breast and no need for maintenance. We show following two choices to the patients.
b-1 Free deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) flap
-
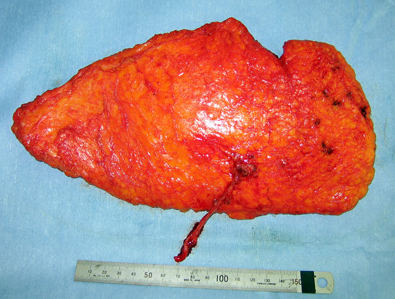
DIEP flap
-
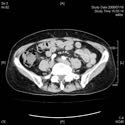
MSCT
DIEP flap is one of the standard option of aoutologous tissue reconstruction. We reduce function loss without injuring a muscle as much as possible. Multislice CT is required before surgery for the vascular evaluation.
b-2 Latissimus dorsi flap / Thoracodorsal artery perforator (TAP) flap
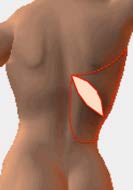
LD flap
It is suitable for small breast. or partial defect after breast conserving surgery.
Nipple areola reconstruction

C-V flap
We reconstruct nipple areola using a local flap (modified C-V flap) and delayed medical tattoo.
Inverted nipple
We recommend conservative treatment. If it is ineffective, surgical intervention is considered.