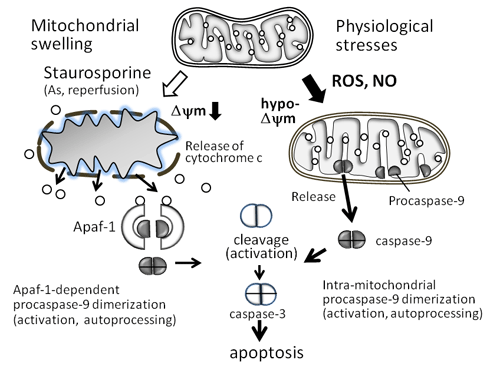
Figure 1. Two modes of mitochondrially controlled initiator caspase-9 activation.
The prevailing model (left) features apoptosome (Apaf-1/(d)ATP/cytochrome c/procaspase-9). The complex is assembled through the mitochondrial damage characterized by the fall of the inner membrane potential (Delta-psi-m), release of cytochrome c, and matrix swelling. Apoptosis by staurosporine may represent this model.
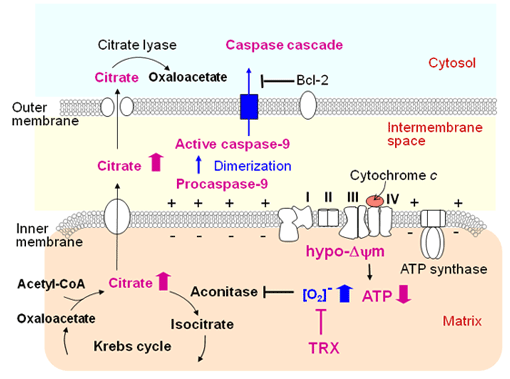
Others and we detected active form caspase-9, as well as procaspase-9, in the intermembrane spacce of the mitochondria before the onset of apoptosis. The hypo-Delta-psi-m condition indicates partial dysfunction of the electron transfer system (respiratory chain) tightly assocaited with the redox regulatory system. Under the oxidative condition, the mitochondrion may activate caspase-9 and release it outside .
Katoh I, Tomimori Y, Ikawa Y, Kurata S. J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 9;279(15):15515-23.